5th floor, Lakshmi Sharada Arcade,
6th Main Road, No 251,
17th Cross Road,Sector 7,
HSR Layout,Bangalore,
Karnataka-560102

The gradual and irreversible brain illness known as Alzheimer's disease has become a major public health concern. Millions of people are impacted globally by it, including those who are diagnosed as well as their family and caregivers. We will delve into the complexities of Alzheimer's in this blog, looking at its causes, symptoms, potential therapies, and ongoing research projects meant to solve the puzzles surrounding this crippling illness.
Definition and the basis:
A neurodegenerative condition called Alzheimer's disease is typified by a slow decline in memory and cognitive function. It is the most typical cause of dementia, a word used to characterize a group of symptoms that are severe enough to interfere with day-to-day functioning and impact thinking, memory, and social functions.
Causes and Risk Factors: Although the precise origin of Alzheimer's disease is still unknown, a number of risk factors have been found by researchers, including age, genetics, family history, and specific lifestyle choices. The biggest risk factor is becoming older; at the age of 65, there is an increased chance of Alzheimer's.
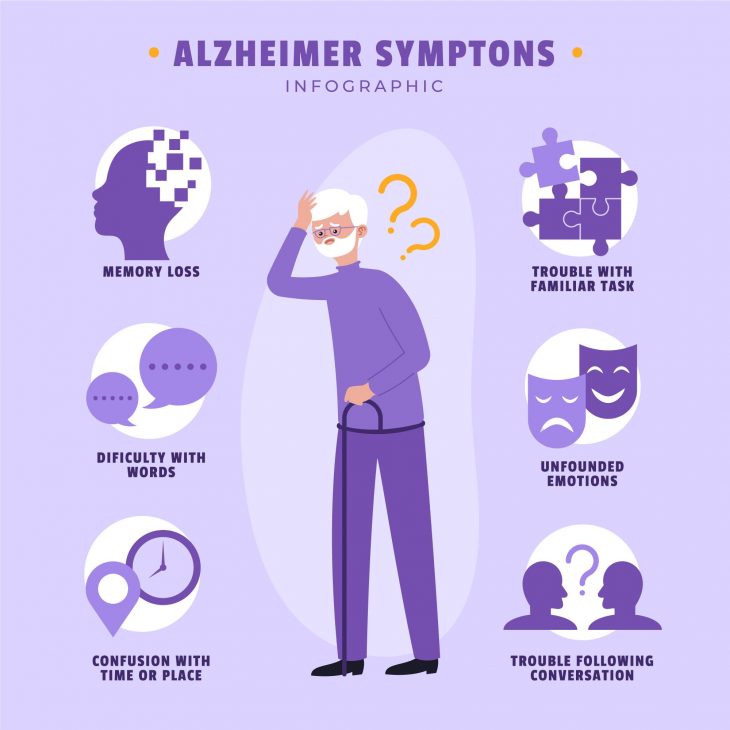
Symptoms and Stages:
Early Symptoms: Confusion, trouble with familiar tasks, and mild forgetfulness are common in the early stages of Alzheimer's disease. It may be difficult to identify these symptoms early on because they can be mild.
Progression: As the illness worsens, people may have more profound memory loss, communication difficulties, and behavioral abnormalities. In advanced phases, basic self-care duties and recognition of loved ones may become impossible.
Treatment Options:
Medication: Although there is still no treatment for Alzheimer's, some drugs can help control symptoms and enhance cognitive performance. Memantine and cholinesterase inhibitors are two typical drugs administered to treat memory and cognitive problems.
Non-Pharmacological Methods: Occupational therapy, speech therapy, and lifestyle changes are examples of complementary methods that can help enhance the quality of life for people with Alzheimer's disease and those who care for them.
Alzheimer's disease poses a significant obstacle for patients, their families, and the international medical community. Addressing the intricacies of this disorder requires a multifaceted approach to care and treatment, increased awareness, and continuous study. Even while there is currently no cure for Alzheimer's, scientific discoveries offer optimism that the disease's secrets will one day be fully solved, opening the door to more potent therapies and, eventually, preventative measures.